In the lab we strive to understand mechanisms of epigenetic regulation in the brain. In particular, we focus on chromatin. Chromatin is the complex of DNA and proteins called histones, which not only package our DNA into complex structures but also control access to our genes. To study histones and how they regulate neuronal function, we combine methods such as microscopy, genome-wide sequencing, bioinformatics, biochemistry, behavioral testing, and more. We have multiple areas of ongoing research in the lab.
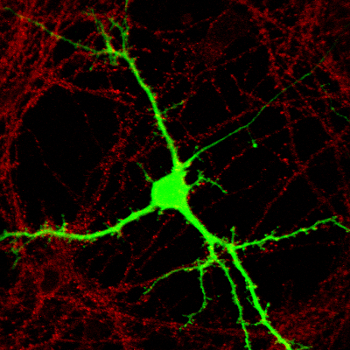
A neuron transfected with GFP allows us to visualize how it changes in response to environmental cues.
The role of histone modifications in regulating how neurons respond to the environment
Histone proteins can be modified by a huge range of posttranslational modifications including phosphorylation, methylation, ubiquitination, and more. These modifications allow histones to respond to different environmental cues and regulate gene expression accordingly. Particularly exciting are several novel modifications only recently discovered in histone proteins. For reasons we don’t yet understand, some of these histone modifications are particularly highly expressed in the brain. We are exploring their regulation and function in neurons and examining how they allow the brain to adapt to a changing environment and new experiences.
The role of different histone variants in learning and memory
Histone proteins can come in different ‘flavors’, or variants. Often these variant proteins only differ by a few amino acids, yet they can play very different roles in regulating transcription. To study the role of these histone variants in the brain, we are applying the tools of chromatin biology such as biochemistry techniques and genome-wide sequencing to the field of neuroscience. We hope to understand how these subtle changes can drastically alter the ability of a neuron to activate the right genes at the right times and allow the brain to perform complex tasks such storing memories and learning new skills.
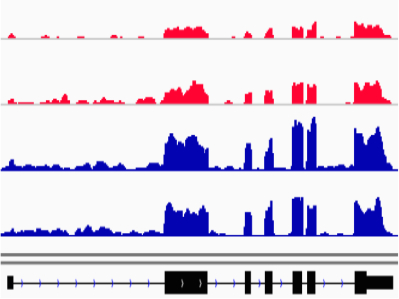
Genome-wide sequencing shows changes in gene expression in response to histones modifications and histone variants.
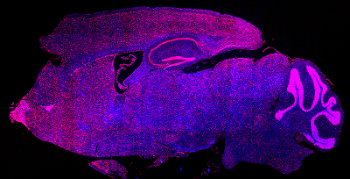
We examine chromatin-regulating proteins in the brain to help explain neurodevelopmental disorders.
The role of chromatin in neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism
Recent studies have identified many new genes linked to autism and other neurodevelopmental disorders. Surprisingly, a large number of these genes encode proteins that are involved in epigenetic regulation. However, in most cases we don’t know how these proteins function in the brain or how their loss can lead to neurodevelopmental disorders. We use a combination of cell culture, genome-wide sequencing, bioinformatics, and behavioral testing of animal models to better understand how these disorders occur and, hopefully, how they can be treated.